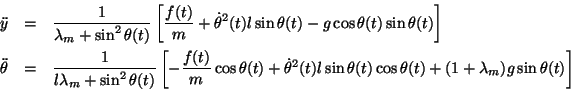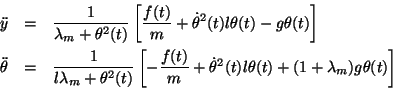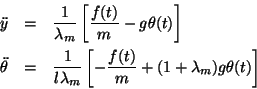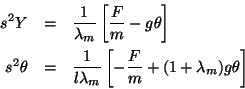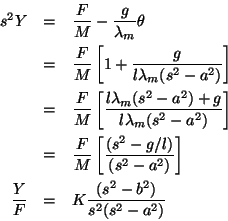|
You are here : Control System Design - Index | Simulations | Inverted Pendulum | Part 1 Inverted Pendulum Tutorial - Part 1System ModelThe modelling of the inverted pendulum system comes straight from simple Newtonian physics. (Note: Modelling is covered in chapter 3 and chapter 4.) This gives us the following equations:
To make the model useful for us, we need to linearize it. Chapter 2
gives one possible procedure for this, but a more heuristic one will be
presented here (which incidentally gives the same result). We first
recognise that
This model is for small variations of
We next take the Laplace transform of these equations (as described in section 3.3).
Now, working with the second equation,
Note that
Recalling the definition of a, we see that
Where b2 = g / l. Using M = m = 0.5, l = 1 and g = 10 we get the following transfer function:
We can see immediately that there is one non-minimum phase zero and an unstable pole. Because of this pole, the system is open-loop unstable (i.e. if we nudge the cart a bit, the mass will fall over). Next, we try to control the inverted pendulum system based on the linear model we have just made. |